Interpreting road surface condition reports
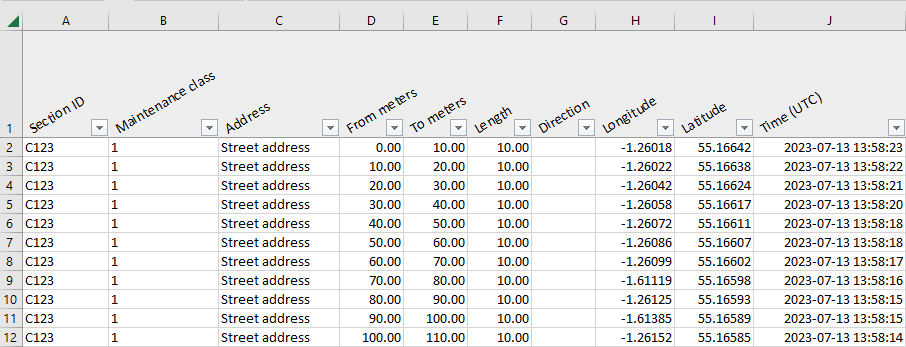
- Section ID
- Maintenance class
- Address
- Examples of customer-specific road network metadata
- From meters
- Start chainage of the interval or segment
- To meters
- End chainage of the interval or segment
- Length
- Interval or segment length
- Direction
- Driving direction (increasing or decreasing chainage), as defined in the road network geometry
- Longitude
- Longitude coordinates (EPSG:4326)
- Latitude
- Latitude coordinates (EPSG:4326)
- Time (UTC)
- Date and time when distress was last detected
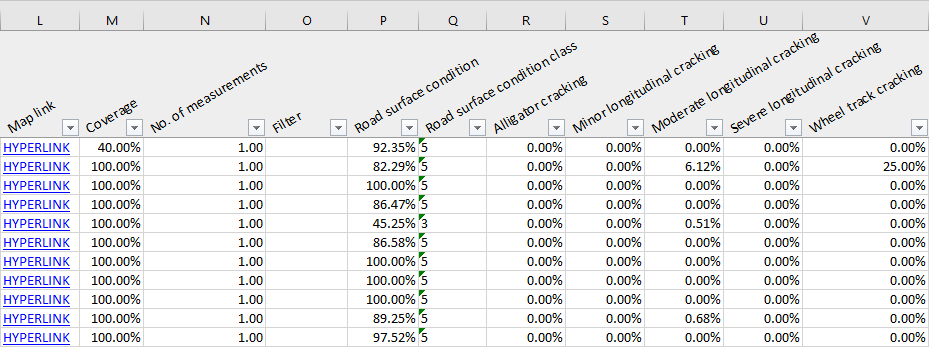
- Map link
- Direct link to map view in RoadAI
- Coverage (total)
- How much of the interval or segment was covered
- No. of measurements
- How many different drives' measurements were used (not necessarily a whole number
because of continuous weighting between measurements from different drives. More recent
drives have a higher relative weight.)
When merging multiple drives together, the time window is two weeks from the most recent video. If the default filters are on, the weather conditions do not affect the weighting because all the data with bad conditions is left out from the report. - Filter
- The filters remove data collected in wet weather, on non-asphalt surfaces or in poor lighting conditions. The Filter column shows why data was removed. For example, it might show Surface condition if the road was wet or Surface type if the road was not asphalt.
 | The parameters selected when creating the report show here. This is an example containing road surface condition data. |
- Road surface condition
- The road surface condition score represents the overall condition of the surface. A score of 100% represents the best possible condition and 0% the worst.
- Road surface condition class
- The road condition class is based on the condition score. By default, a score of 0‑20 % results in class 1, 21‑40 % in class 2, 41‑60 % in class 3, 61‑80 % in class 4, and 81‑100 % in class 5.
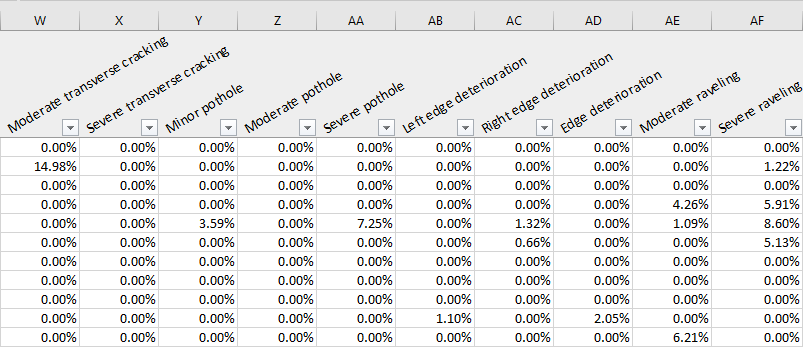
- Alligator cracking
- Minor longitudinal cracking
- Moderate longitudinal cracking
- Severe longitudinal cracking
- Wheel track cracking
- Moderate transverse cracking
- Severe transverse cracking
- Minor pothole
- Moderate pothole
- Severe pothole
- Left edge deterioration
- Right edge deterioration
- Edge deterioration
- Moderate raveling
- Severe raveling
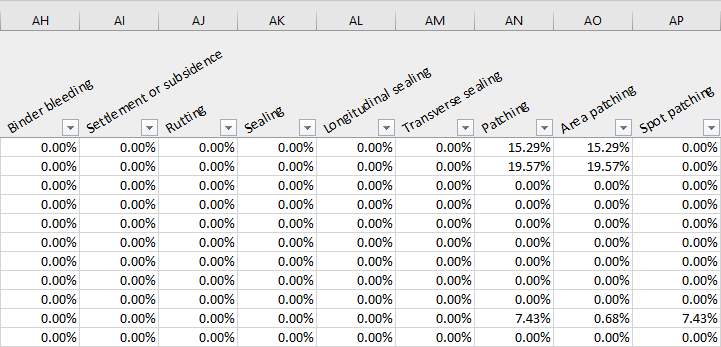
- Binder bleeding
- Subsidence
- Rutting
- Crack sealing
- Longitudinal crack sealing
- Transverse crack sealing
- Area patching
- Spot patching
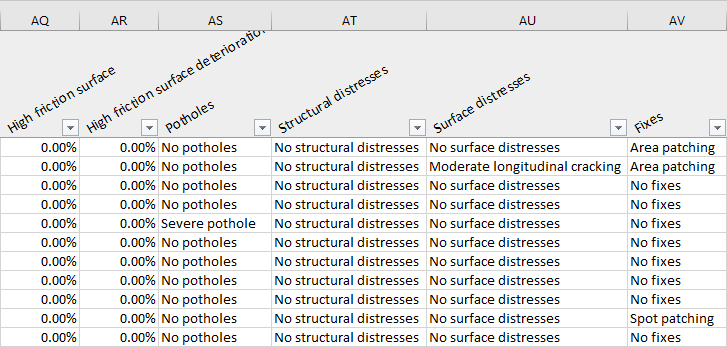
- High friction surface
- High friction surface deterioration
- The percentage is the severity value of the distress. This value is aggregated according to the choices made during the report creation phase.
- Potholes
- If potholes were detected
- Structural distresses
- If structural distresses were detected, and their type
- Surface distresses
- If structural distresses were detected, and their type
- Fixes
- If fixes were detected, and their type
